Company News
CHAENG Show the Lime Production Equipment Working Principle

Building air-hardening lime is a product made from calcareous and calcerous magnesium carbonate rocks by their calcination up to the point when carbon dioxide is completely removed from them. It mostly consists of calcium oxide. Depending on the ratio of calcium and magnesium oxide content, lime can be high-calcium, high-magnesium, and dolomitic. It is produced as non-slaked (anhydrous) and slaked (hydrated) lime. Hydraulic lime can be high-hydraulic or low-hydraulic.
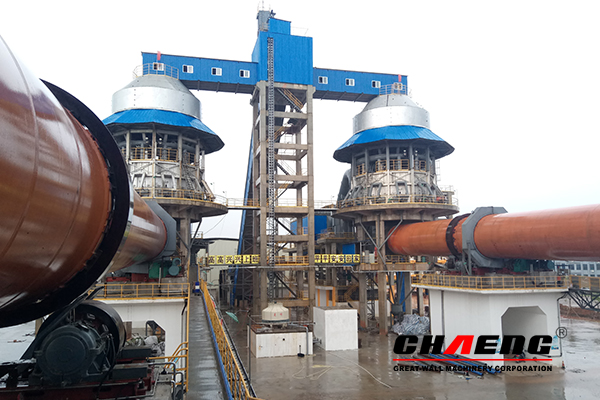

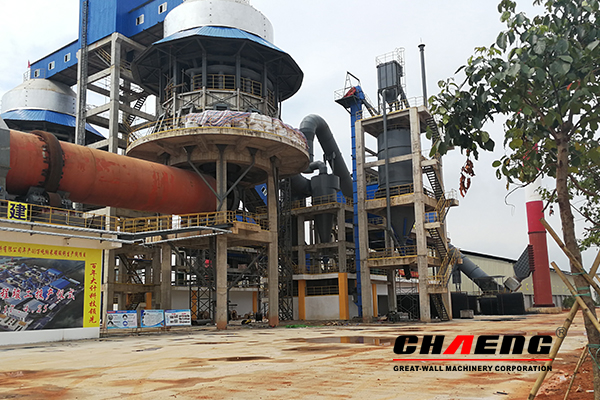
The main process in the lime production is the limestone calcination. It is preceded by crushing of lime stone to 20 to 40 mm in size for the purposes of calcination in rotary furnaces, and to 40 to 70 mm in size for the purposes of calcination in shaft furnaces. At the moment, the Strommashina plant in Samara does not manufacture equipment for producing lime in fluidized bed furnaces. Limestone is calcinated in various furnaces: shaft, rotary, fluidized bed furnaces, using suspension roasting process, etc. The most common furnace type is shaft and rotary furnaces. The former — shaft type overturning lime calcination furnaces — are somewhat more fuel-saving, but lime appears to be contaminated with fuel ash. Also, due to larger particle size subjected to heat treatment, some lumps are left under-calcinated (underburning), while some are over-calcinated (overburning).